Cerebral angiography is a diagnostic procedure commonly done for the diagnosis and evaluation of various vascular lesions of the brain like aneurysm, arteriovenous malformation, dural-AVM, occlusion of the brain artery, collateral circulation in brain artery occlusion to define need for the intervention etc.
This procedure is generally performed under local anaesthesia. A needle puncture is done in the groin to access the artery of the groin(femoral artery) and then cannulated with a back-lock femoral sheath. Through this femoral sheath a catheter (thin, long tube) is navigated through the aorta into the brain arteries (carotid and vertebral arteries). Subsequent to this a dye (radio-opaque, water soluble iodinated contrast) is injected in the brain artery to cine imaging is performed to obtain pictures in various planes using advanced neurovascular cathlab. Theses images are then carefully analysed and if needed then three dimensional rotating angiogram can be performed in a few seconds time to obtain a very clear high resolution images which can pick up even micro aneurysm of 1mm in size.
Cerebral angiography (DSA) is generally a day-care procedure in which in which patient arrive hospital on a scheduled day in an overnight fasting state and after initial clinical assessment and preparation including consent for the procedure, patient is shifted to the Neurointervnetion Cathlab. After the procedure the catheter is removed and puncture site is given manual compression for a few minutes to stop bleeding from the punctured femoral artery. patient is then shifted to the ICU/Day-care for monitoring and after 6 hours of the procedure, patient is generally discharged for the home.
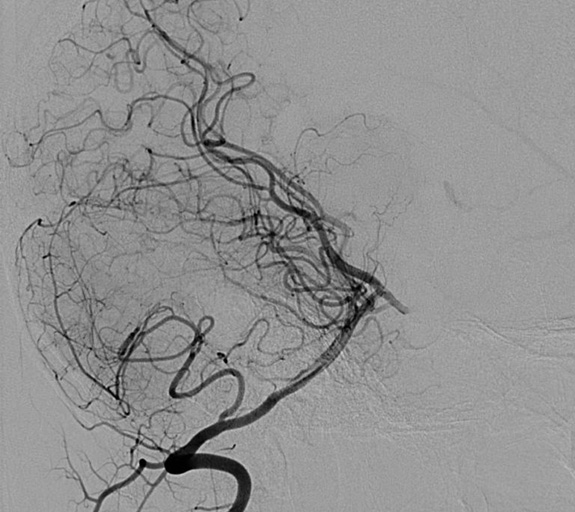
Vertebral artery angiogram showing normal intracranial blood vessels
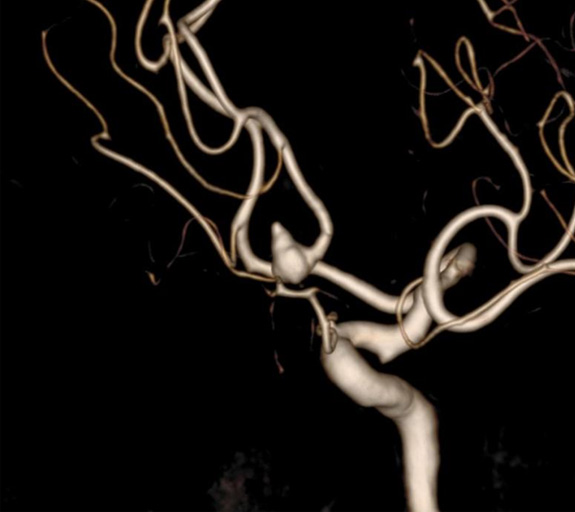

Left internal carotid 3D-RA showing an AComA aneurysm
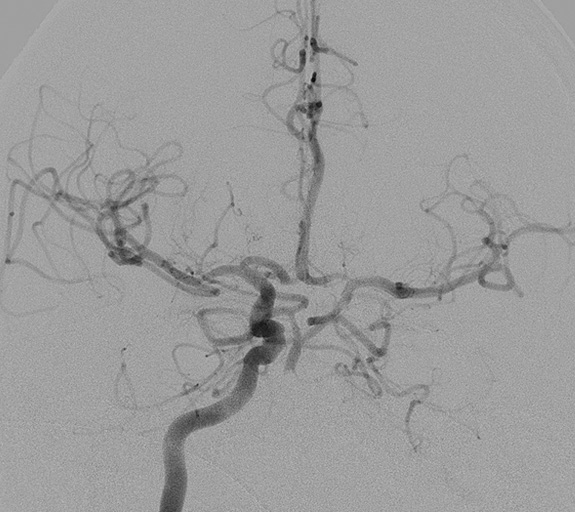
right Carotid artery angiogram showing a cross flow to left carotid in an occluded left carotid artery
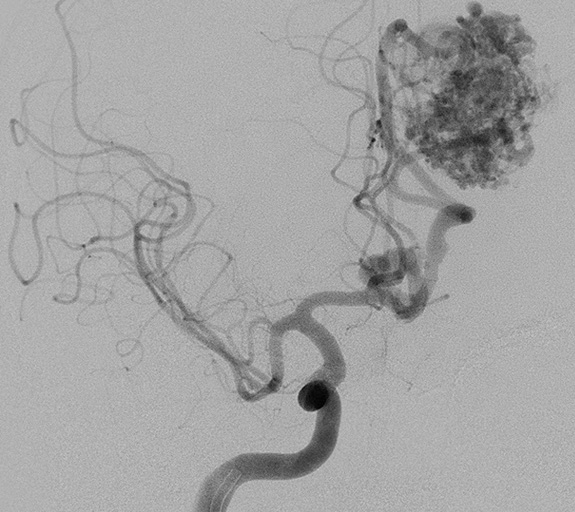
Right Carotid artery angiogram showing an AVM located in left carotid artery territory
Spinal angiography is almost similar to the cerebral angiography except the neurointervntionist has to catheterise multiple segmental arteries along each vertebral levels. In a complete spinal angiogram one has to catheterise and perform angiogram through 12 thoracic, 5 lumber and three sacral segmental arteries apart from two vertebral and two subclavian arteries. Because of this it becomes a long procedure and require immense co-operation of the patient. Therefore, often it is performed under general anaesthesia. Common indications for Spinal DSA includes:
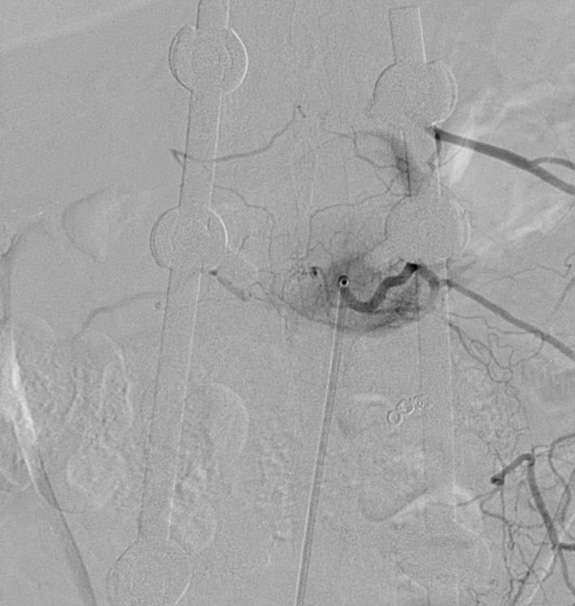
Normal Spinal DSA after contrast injection to left D8 segmental artery
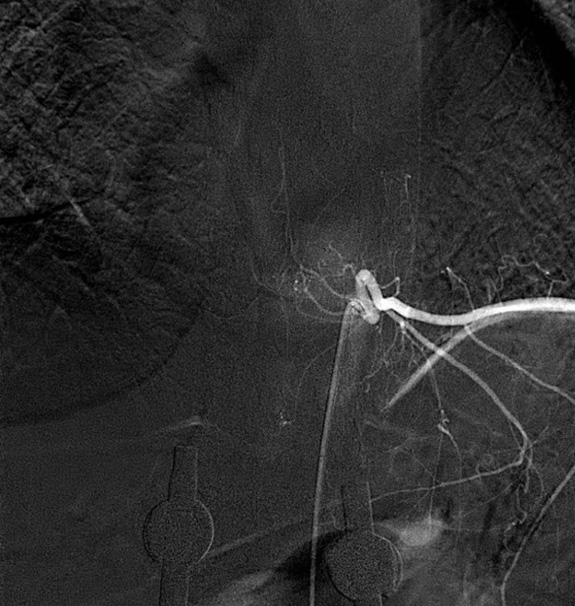
Spinal DSA after contrast injection to left D10 segmental artery showing anterior spinal artery./p>